And Why Their Failure Stops Your Laundry
The Silent Power Couriers Inside Your Washer
① The Core Mechanism – Simplifie
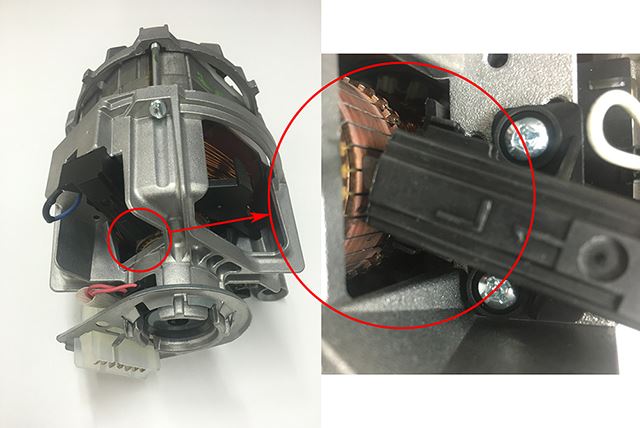
Carbon brushes are the motor’s electricity delivery team. Think of them as two spring-loaded graphite “fingers” (see highlighted image below) that:
- Press against the spinning armature (a copper coil cylinder)
- Transfer electricity from the power source to the armature
- Create electromagnetic force that makes the armature – and ultimately the drum – rotate via the drive belt.
Key Design Insight
Their spring mechanism acts like a persistent handshake, ensuring constant contact even as the armature spins at high speed.
② What Happens When They Wear Out?
The Domino Effect of Worn Brushes
- Stage 1: Graphite erosion from friction reduces brush length → Springs can’t compensate anymore.
- Stage 2: Intermittent sparking occurs → Electricity transfer becomes unstable.
- Stage 3: Complete disconnection → Motor loses power → Drum freezes mid-cycle.
You’ll Know It’s Them If
✅ Machine fills with water but drum doesn’t budge
✅ Wash/spin cycles “run” silently (no motor hum)
✅ Clothes emerge soaking wet despite “completed” cycle
③ Why Carbon Brushes Fail Faster Than Other Parts
(Builds Technical Credibility)
| Factor | Impact on Carbon Brushes | Typical Lifespan* |
|---|---|---|
| High Friction | Constant rubbing against armature | 5-8 years |
| Water Exposure | Steam degrades spring tension | 3-5 years |
| Overloading | Extra strain increases wear rate | 2-4 years |
Based on LG/Samsung service data for standard home use.
④ Quick Diagnostic Guide
Before You Buy Replacements
- Locate the brushes: Usually behind a panel near the motor (consult manual)
- Measure them: New brushes = ~1.5 inches; Replace if < 0.25 inches
- Check for damage: Cracked brushes or corroded springs mean immediate replacement
Pro Tip
Take a photo of brush orientation before removal – incorrect installation can damage the armature!
⑤ Beyond Carbon Brushes: Other Common Drum Stoppers
While 60% of drum failures stem from brushes (Appliance Repair Journal, 2023), also consider:
- 🔗 Faulty Drive Belt: Learn how to check tension
- 🔗 Blocked Pump: Signs of drainage issues
- 🔗 Control Board Errors: Diagnose error codes




